Migraines: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments for Long-Term Relief
Migraines can be debilitating, with pounding headaches, nausea, and sensitivity to light and sound causing immense discomfort. Understanding the triggers, such as stress, certain foods, or hormonal changes, can help manage and prevent these attacks.
Introduction
Migraines are more than just headaches; they are debilitating neurological conditions that affect millions of people worldwide. If you've ever experienced a migraine, you know how excruciating and disruptive it can be. But what causes migraines, and how can you prevent or manage them effectively? In this comprehensive guide, we explore the causes, symptoms, triggers, and the best treatment options available to help you achieve long-term relief.
What Are Migraines?
Migraines are intense headaches that can last for hours or even days. They are often accompanied by symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. Unlike regular headaches, migraines involve complex neurological changes that can significantly impact daily life.
Common Causes of Migraines
1. Genetic Factors
Studies suggest that genetics play a crucial role in migraines. If one or both of your parents suffer from migraines, you are more likely to experience them.
2. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, especially in women, can trigger Migraines. Many women experience migraines around their menstrual cycle, pregnancy, or menopause due to shifts in estrogen levels.
3. Stress and Anxiety
Chronic stress and anxiety can trigger migraines by causing tension in the muscles and affecting neurotransmitter levels in the brain.
4. Diet and Nutrition
Certain foods and drinks, such as processed foods, caffeine, alcohol, and artificial sweeteners, can trigger migraines. A balanced diet can help reduce the frequency of migraine attacks.
5. Sleep Patterns
Lack of sleep or irregular sleep patterns can contribute to migraines. Ensuring a consistent sleep schedule can help in migraine prevention.
6. Environmental Factors
Weather changes, bright lights, strong smells, and loud noises can act as migraine triggers.
Recognizing Migraine Symptoms
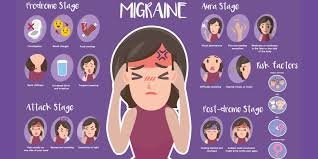
Migraines usually occur in four stages:
1. Prodrome Stage
This phase occurs a few hours or days before a migraine and includes:
-
Mood swings
-
Food cravings
-
Neck stiffness
-
Frequent yawning
2. Aura Stage
Some people experience visual disturbances, such as flashing lights, blind spots, or tingling sensations before the headache begins.
3. Attack Stage
The migraine itself lasts between 4 to 72 hours and includes:
-
Throbbing pain, usually on one side of the head
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Sensitivity to light, sound, and smell
4. Postdrome Stage
After the headache subsides, people may feel drained, confused, and exhausted for up to 24 hours.
Effective Treatments for Migraines
1. Medications
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
-
Ibuprofen
-
Acetaminophen
-
Aspirin
Prescription Medications
-
Triptans (e.g., sumatriptan)
-
Ergots (e.g., dihydroergotamine)
-
CGRP inhibitors (e.g., fremanezumab)
2. Natural Remedies
Essential Oils
Peppermint and lavender oils can help reduce headache severity when applied to the temples.
Herbal Supplements
-
Feverfew and butterbur are known to reduce migraine frequency.
-
Magnesium and riboflavin (Vitamin B2) may also be beneficial.
3. Lifestyle Changes for Long-Term Relief
Healthy Diet
-
Avoid trigger foods (e.g., processed meats, aged cheese, artificial sweeteners)
-
Stay hydrated
Regular Exercise
Moderate physical activity, such as yoga and walking, can reduce stress and prevent migraines.
Stress Management Techniques
-
Meditation
-
Deep breathing exercises
-
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Sleep Hygiene
-
Maintain a regular sleep schedule
-
Avoid electronic screens before bedtime
4. Alternative Therapies
Acupuncture
This traditional Chinese practice has shown promise in reducing migraine frequency.
Massage Therapy
Regular massages can help reduce the tension that contributes to migraines.
Biofeedback Therapy
This technique teaches individuals to control physiological functions to reduce stress and prevent migraines.
When to See a Doctor
You should consult a healthcare professional if:
-
Your migraines occur frequently and interfere with daily life.
-
You experience new or worsening symptoms.
-
Your headache is sudden and severe.
-
You have neurological symptoms such as confusion, vision loss, or difficulty speaking.
Conclusion
Migraines are complex but manageable with the right strategies. Identifying triggers, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and seeking appropriate treatments can significantly reduce migraine frequency and intensity. If you suffer from chronic migraines, consult a healthcare provider for a tailored treatment plan to improve your quality of life.
What's Your Reaction?














