Mapping the Brain: Advancements in Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
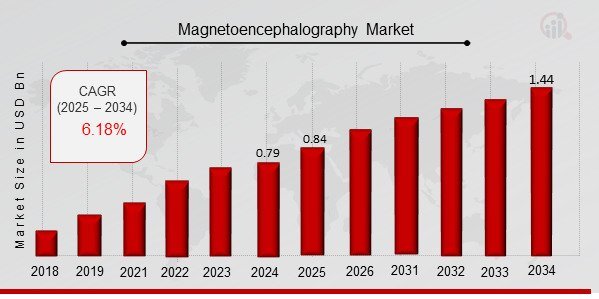
Magnetoencephalography Market Size was estimated at 0.79 (USD Billion) in 2024. The Magnetoencephalography Market Industry is expected to grow from 0.84 (USD Billion) in 2025 to 1.44 (USD Billion) till 2034, at a CAGR (growth rate) is expected to be around 6.18% during the forecast period (2025 - 2034).
Introduction: Unveiling Neural Dynamics with Non-Invasive Brain Activity Mapping and High Spatiotemporal Resolution
The Magnetoencephalography (MEG) Market is driving transformative advancements in neurological diagnostics and neuroscience research by providing non-invasive, high-resolution mapping of brain activity. MEG systems detect the minute magnetic fields generated by the electrical currents flowing within neurons, offering unparalleled spatial and temporal resolution compared to other neuroimaging techniques. This capability enables researchers and clinicians to delve into the intricate dynamics of brain function, unraveling the neural basis of cognition, behavior, and neurological disorders.
Mechanisms of Action: Superconducting Quantum Interference Devices (SQUIDs) and Magnetic Field Detection
MEG systems employ highly sensitive superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDs) to detect the extremely weak magnetic fields generated by neuronal activity. These SQUIDs are housed within a magnetically shielded room to minimize interference from external magnetic fields. The MEG system maps brain activity with millisecond-level temporal resolution, capturing the rapid fluctuations in neural activity, and millimeter-level spatial resolution, precisely localizing the sources of these fluctuations. This combination of high spatiotemporal resolution provides a dynamic and detailed picture of brain function, allowing for the study of neural processes in real-time.
Applications in Epilepsy Localization: Precise Identification of Seizure Foci for Surgical Planning
MEG plays a crucial role in the pre-surgical evaluation of patients with epilepsy, particularly those with drug-resistant seizures. By precisely localizing the seizure onset zone (SOZ), MEG helps neurosurgeons plan surgical resections that minimize damage to healthy brain tissue. This improves surgical outcomes and reduces the risk of post-operative neurological deficits. MEG can also identify epileptogenic networks that are not visible on other imaging modalities, providing valuable information for surgical planning and patient management.
Brain Tumor Mapping and Pre-Surgical Planning: Minimizing Neurological Deficits During Resection
MEG helps map eloquent cortex areas, such as motor, sensory, and language areas, located near brain tumors. This information guides surgical resection, minimizing damage to these critical brain regions and preserving neurological function. By identifying the functional boundaries of eloquent cortex, MEG helps neurosurgeons plan surgical approaches that maximize tumor removal while minimizing post-operative neurological deficits.
Cognitive Research: Understanding Brain Function, Connectivity, and Neural Dynamics
Researchers use MEG to study a wide range of cognitive processes, including perception, attention, memory, language, and decision-making. MEG's high temporal resolution allows for the study of the dynamic changes in brain activity associated with these processes. MEG can also map brain connectivity, revealing the functional networks that underlie cognitive function. These insights advance our understanding of the neural basis of cognition and behavior, contributing to the development of new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Improved Spatial Resolution: Precise Localization of Brain Activity Sources
MEG offers superior spatial resolution compared to electroencephalography (EEG), allowing for more precise localization of the sources of brain activity. This is particularly important for localizing deep brain structures and distinguishing between closely spaced neural generators. The improved spatial resolution of MEG enhances the accuracy of diagnostic and research findings.
Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy: Early Detection and Management of Neurological Disorders
Enhanced diagnostic accuracy aids in the early detection and management of a wide range of neurological disorders, including epilepsy, brain tumors, stroke, and traumatic brain injury. MEG can detect subtle changes in brain activity that may not be apparent on other imaging modalities, enabling early intervention and improved patient outcomes.
Magnetoencephalography Market Overview
As per MRFR analysis, the Magnetoencephalography Market Size was estimated at 0.79 (USD Billion) in 2024. The Magnetoencephalography Market Industry is expected to grow from 0.84 (USD Billion) in 2025 to 1.44 (USD Billion) till 2034, at a CAGR (growth rate) is expected to be around 6.18% during the forecast period (2025 - 2034).
Challenges and Future Directions: High Cost, Sensitivity to Artifacts, Portable MEG, and AI Integration
Despite its numerous advantages, the MEG market faces several challenges. These include the high cost of MEG systems, their sensitivity to environmental magnetic interference, and the need for specialized magnetically shielded rooms. Future directions focus on developing portable MEG systems that do not require shielded rooms, integrating AI for automated data analysis and artifact removal, and improving sensor technology to enhance sensitivity and reduce cost. These advancements will make MEG more accessible and user-friendly, expanding its applications in clinical and research settings.
Conclusion: Transforming Neurological Diagnostics and Neuroscience Research with Detailed Brain Function Insights
MEG is transforming neurological diagnostics and neuroscience research by providing detailed insights into brain function, connectivity, and neural dynamics. Its high spatiotemporal resolution and non-invasive nature make it a powerful tool for studying the human brain in health and disease. As technology continues to advance, MEG will play an increasingly important role in improving patient outcomes and advancing our understanding of the brain.
What's Your Reaction?

















