How to Prevent Giardiasis: Simple Tips for Staying Healthy?
Giardiasis is a parasitic infection caused by Giardia lamblia, a microscopic parasite that can wreak havoc on the digestive system.
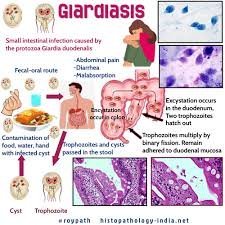
Giardiasis is a parasitic infection caused by Giardia lamblia, a microscopic parasite that can wreak havoc on the digestive system. This illness is often contracted by consuming contaminated water or food, or through direct contact with an infected individual.
While it can cause uncomfortable symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal cramps, and nausea, the good news is that giardiasis is preventable. By adopting specific hygiene practices and being cautious about what you eat and drink, you can significantly reduce your risk of infection.
In this guide, we will explore effective measures to prevent giardiasis and discuss the role of medications like Nizonide in managing the infection.
1. Understand the Transmission of Giardiasis
Giardiasis spreads through the ingestion of Giardia cysts, which are resistant forms of the parasite that can survive in harsh environmental conditions. These cysts are commonly found in
- Contaminated water sources, such as lakes, rivers, and poorly treated municipal water supplies.
- Contaminated food prepared by infected individuals who have not practiced proper hygiene.
- Surfaces or objects that have been touched by an infected person.
- Understanding these transmission routes can help you take proactive steps to avoid exposure.
2. Prioritize Safe Drinking Water
Waterborne transmission is one of the most common ways giardiasis spreads. To ensure safe drinking water
- Always use filtered or boiled water when traveling to areas with questionable water quality.
- Invest in a reliable water filtration system for your home, particularly if you live in areas prone to water contamination.
- Avoid drinking directly from natural water sources such as rivers or lakes, even if they appear clean.
- Use water purification tablets or portable filters when camping or hiking.
3. Practice Proper Food Hygiene
Food can also become contaminated with Giardia if it is handled improperly. To reduce the risk
- Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly under running water before consuming them.
- Avoid eating raw or undercooked foods, particularly in areas where food safety regulations are lax.
- Ensure that individuals preparing your meals practice good hygiene, including washing their hands and cleaning kitchen surfaces regularly.
4. Maintain Good Personal Hygiene
Personal hygiene plays a crucial role in preventing the spread of giardiasis
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially after using the restroom, before eating, and after handling pets.
- Teach children proper handwashing techniques, as they are often more susceptible to infections.
- Avoid biting your nails or putting your hands in your mouth, particularly if you’ve been in public spaces.
- Use hand sanitizers as a backup when soap and water are not available, although they may not be as effective against Giardia cysts.
5. Avoid Contact with Infected Individuals
Giardiasis can spread through person-to-person contact. To minimize this risk
- Avoid sharing utensils, towels, or other personal items with someone who has giardiasis.
- If you are caring for an infected individual, use gloves when cleaning up after them and wash your hands thoroughly afterward.
- Encourage infected individuals to stay home until they have fully recovered to prevent the spread of the infection in community settings.
6. Educate Yourself About High-Risk Areas
Certain regions have higher rates of giardiasis due to poor sanitation and water quality. If you are traveling to such areas
- Research the local water and food safety conditions beforehand.
- Stick to bottled or boiled water and avoid ice cubes made from untreated water.
- Choose restaurants and eateries with a reputation for cleanliness and hygiene.
7. Use Medications When Necessary
If you suspect you have contracted giardiasis, consult a healthcare professional promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and reduce the likelihood of spreading the infection to others.
One commonly prescribed medication for treating giardiasis is nizonide. This medication contains nitazoxanide, which is effective in eradicating Giardia parasites from the body. While Nizonide is generally well-tolerated, it is essential to follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment.
Nizonide works by interfering with the energy production of the parasites, ultimately killing them. It is particularly useful in cases where patients have recurrent or severe giardiasis. However, prevention remains the best strategy, as avoiding infection altogether reduces the need for medication.
8. Protect Vulnerable Populations
Certain groups, such as young children, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems, are more vulnerable to giardiasis. To protect these populations
- Ensure they have access to clean drinking water and properly prepared food.
- Educate caregivers about the importance of hygiene and safe food handling.
- Monitor their health closely and seek medical advice promptly if symptoms of giardiasis appear.
9. Stay Informed About Community Outbreaks
In some cases, giardiasis outbreaks can occur due to contaminated municipal water supplies or food sources. Stay informed by
- Following local health advisories and alerts.
- Participating in community discussions about water safety and sanitation improvements.
- Advocating for better infrastructure to ensure safe water and food supply systems.
10. Regularly Clean and Disinfect Surfaces
Giardia cysts can survive on surfaces for extended periods. To minimize the risk of transmission within your home
- Clean high-touch surfaces regularly using disinfectants that are effective against parasites.
- Wash bedding, towels, and clothing used by infected individuals in hot water.
- Sanitize items such as toys and utensils that may come into contact with children.
Final Thoughts
Preventing giardiasis requires a combination of vigilance, education, and good hygiene practices. By understanding the transmission routes and adopting preventative measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of contracting this unpleasant infection. In cases where prevention falls short, medications like Nizonide offer an effective solution for treatment, enabling quick recovery and minimizing the spread of the parasite.
Stay proactive about your health and encourage those around you to adopt similar practices. A clean and cautious lifestyle is your best defense against giardiasis and other waterborne diseases.
What's Your Reaction?















