Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Cause Muscle Pain?
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints. However, many RA patients also experience muscle pain and weakness.
Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints. However, many RA patients also experience muscle pain and weakness. But is muscle pain a direct symptom of RA, or does it stem from other factors?
The short answer is yes—RA can contribute to muscle pain, but it usually happens indirectly due to inflammation, medication side effects, or lack of mobility. Understanding this connection is crucial for finding effective relief. In this article, we will explore the link between RA and muscle pain, discuss treatment options, and highlight how medications like Pain O Soma 500 mg can help manage discomfort.
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
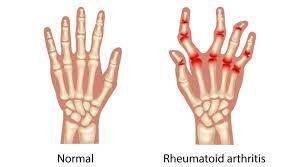
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s joints. This leads to inflammation, swelling, and pain. Over time, RA can cause joint deformities and loss of function.
How RA Affects the Body
RA is not just a joint disease—it also affects the muscles, tendons, and connective tissues. Chronic inflammation can weaken surrounding muscles, leading to pain and stiffness.
Who is at Risk for RA?
Anyone can develop RA, but certain factors increase the risk:
- Genetics: A family history of RA increases the likelihood.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop RA than men.
- Age: RA typically appears between ages 30 and 60.
- Smoking: Increases the risk and worsens symptoms.
Common Symptoms of RA
- Joint pain and swelling
- Stiffness (especially in the morning)
- Fatigue and weakness
- Loss of joint function
- Muscle pain and tenderness
Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Cause Muscle Pain?
The Link Between RA and Muscle Pain
Muscle pain in RA is not as well-known as joint pain, but it is a common issue. Inflammation from RA can extend beyond the joints, affecting the muscles and causing pain.
How RA Inflammation Affects Muscles
RA causes the immune system to attack healthy tissues, leading to chronic inflammation. This inflammation can spread to the muscles, causing soreness and stiffness.
Muscle Weakness and Atrophy Due to RA
As RA progresses, patients may move less due to joint pain, leading to muscle weakness (atrophy). When muscles aren’t used regularly, they become weaker, increasing pain and discomfort.
RA’s Impact on Mobility and Daily Life
Muscle pain can make it difficult to perform everyday activities like walking, lifting objects, or even getting out of bed. Over time, this can reduce the overall quality of life.
Other Causes of Muscle Pain in RA Patients
1. Medication Side Effects
Some RA medications, such as corticosteroids, can contribute to muscle weakness and cramps.
2. Lack of Physical Activity
Many RA patients avoid movement due to pain, which leads to muscle stiffness and deconditioning.
3. Co-Existing Conditions (Fibromyalgia, Lupus, etc.)
RA patients often develop fibromyalgia, a condition that causes widespread muscle pain and tenderness.
4. Poor Posture and Joint Misalignment
As joints weaken, posture can be affected, putting extra strain on muscles and causing pain.
How to Manage Muscle Pain in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Pain Relief Medications – Try Pain O Soma 500 mg
Muscle relaxants like Pain O Soma 500 mg help relieve muscle pain and improve mobility.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Muscle Pain
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Stay hydrated
- Reduce stress levels
Physical Therapy and Exercise
- Strength training helps maintain muscle mass
- Yoga and stretching improve flexibility
Heat and Cold Therapy for Muscle Relief
- Heat therapy: Relaxes stiff muscles
- Cold therapy: Reduces inflammation and numbs pain
The Role of Medications in Treating Muscle Pain
- DMARDs: Slow RA progression
- NSAIDs: Reduce inflammation
- Corticosteroids: Provide quick relief
- Muscle Relaxants: Pain O Soma 500 mg helps ease discomfort
Home Remedies for Muscle Pain in RA
1. Anti-Inflammatory Foods and Herbal Supplements
- Turmeric, ginger, and omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation.
2. The Benefits of Massage and Acupuncture
- These therapies improve circulation and relieve muscle tension.
3. Stress Management and Relaxation Techniques
- Meditation and breathing exercises can ease tension and pain.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if:
- Muscle pain becomes severe
- RA symptoms worsen despite treatment
- You experience sudden muscle weakness
Conclusion
Rheumatoid arthritis can cause muscle pain due to inflammation, medication side effects, and inactivity. Managing this pain requires a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. If muscle pain affects your daily life, talk to your doctor about treatments like Pain O Soma 500 mg to improve mobility and comfort.
What's Your Reaction?















